Introduction: Why Vitamins & Supplements Matter
Where healthy diets are often compromised by convenience and time constraints, vitamins and supplements have become essential tools to ensure we meet our nutritional needs. With countless options on the market, understanding which vitamins and supplements can support our health can be challenging. This article dives deep into the world of vitamins and supplements, exploring their benefits, potential risks, and how to integrate them into your wellness routine effectively.
Table of Contents
Vitamins & Supplements

Understanding Vitamins & Supplements
- Vitamins: Essential organic compounds that our bodies need to function properly. They support numerous functions, from boosting immunity to enhancing skin health.
- Supplements: Products designed to fill in the gaps where our diet may fall short, providing concentrated amounts of vitamins, minerals, and other beneficial compounds like omega-3 fatty acids, probiotics, or amino acids.
Top Essential Vitamins and Their Benefits
| Vitamin | Primary Benefits | Common Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin A | Supports vision, immune function, skin health | Carrots, sweet potatoes, spinach |
| Vitamin C | Boosts immunity, aids in collagen production, antioxidant | Oranges, strawberries, bell peppers |
| Vitamin D | Supports bone health, immune system | Sunlight exposure, fortified milk, fish |
| Vitamin E | Antioxidant, supports skin health and immune function | Nuts, seeds, green leafy vegetables |
| Vitamin K | Essential for blood clotting and bone health | Kale, broccoli, spinach |
| B Vitamins | Energy production, brain health, red blood cell formation | Whole grains, meat, eggs, legumes |
Why These Vitamins Are Important
Each vitamin has unique functions and benefits for our body, impacting everything from energy levels to bone health. For instance, Vitamin D has recently gained popularity for its role in immune support, particularly during winter months when sun exposure is limited.
Minerals Essential to Health
| Mineral | Primary Benefits | Common Food Sources |
|---|---|---|
| Calcium | Essential for bone and teeth health | Dairy, leafy greens, almonds |
| Iron | Supports oxygen transport in the blood | Red meat, beans, tofu |
| Magnesium | Aids muscle function, sleep, and energy production | Nuts, seeds, whole grains |
| Potassium | Supports heart and kidney function | Bananas, oranges, potatoes |
| Zinc | Enhances immune function and wound healing | Meat, shellfish, legumes |
The Role of Minerals in Supplementation
Minerals, like vitamins, are crucial to health, yet deficiencies are common due to modern diets. For example, magnesium is often lacking, even though it plays a role in over 300 bodily functions, from muscle relaxation to sleep quality.
Popular Supplements Beyond Vitamins and Minerals
- Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Found in fish oil, these are essential for heart and brain health. - Probiotics
Beneficial bacteria that support gut health, which can influence digestion, mood, and immunity. - Collagen
Supports skin elasticity, joint health, and bone strength. - Multivitamins
Offer a combination of essential vitamins and minerals, often tailored to specific needs (e.g., for men, women, seniors, etc.).
Statistics on Vitamins & Supplements Use
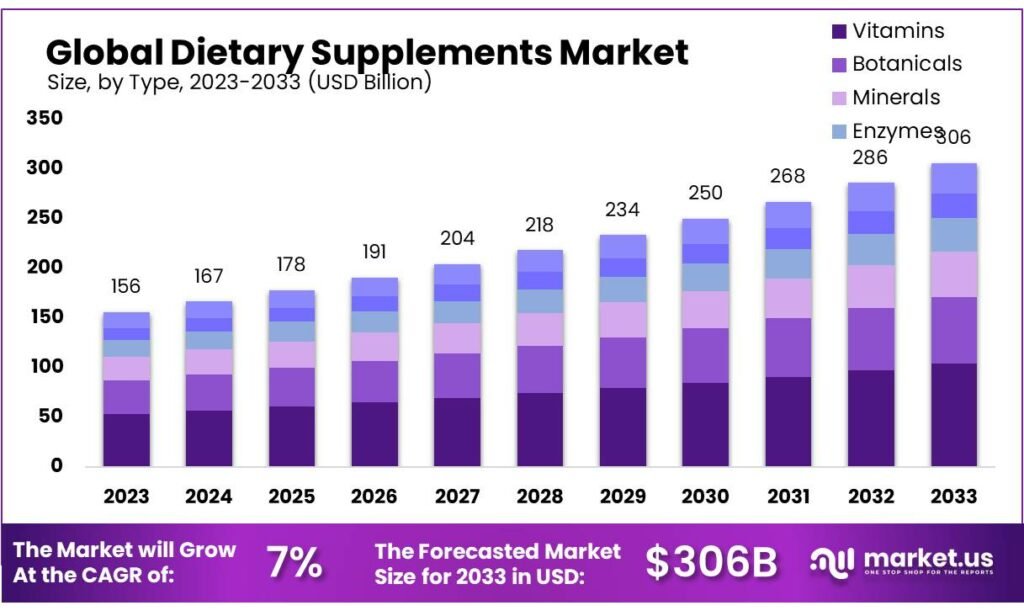
The popularity of vitamins & supplements continues to rise globally. According to a recent survey by the Council for Responsible Nutrition:
- 77% of Americans report using dietary supplements regularly.
- 73% of users believe supplements are an integral part of overall health.
- 50% of Americans say they are more health-conscious since the COVID-19 pandemic.
These numbers underscore a widespread belief in the importance of supplementation for long-term health benefits.
Who Needs Vitamins & Supplements? Understanding Your Individual Needs
While most people can benefit from some form of supplementation, the following groups may particularly benefit:
- Pregnant Women: May need folic acid, iron, and calcium.
- Vegans and Vegetarians: Often require Vitamin B12, iron, and omega-3 supplements.
- Older Adults: May need higher doses of calcium, Vitamin D, and B vitamins.
- Athletes: May benefit from protein, creatine, and electrolyte supplementation.
Choosing Quality Supplements
- Look for Third-Party Testing: Choose products verified by organizations like NSF, USP, or ConsumerLab to ensure purity and quality.
- Check for Fillers: Avoid supplements with unnecessary additives, sugars, or artificial colors.
- Bioavailability: Some forms of vitamins are more bioavailable than others (e.g., magnesium citrate over magnesium oxide).
Vitamins & Supplements: Safety and Potential Risks
- Over-supplementation: Excessive intake, particularly of fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), can lead to toxicity.
- Interactions with Medications: Some supplements may interact with medications. For example, calcium can interfere with certain antibiotics.
- Consult a Healthcare Provider: Especially if you are pregnant, nursing, or have chronic health conditions.
Tips for a Balanced Supplement Regimen

- Get Tested First: Testing can reveal deficiencies, helping you tailor your supplements accordingly.
- Follow the Dosage: More isn’t always better, particularly with potent nutrients like Vitamin A or iron.
- Stay Informed: Research the latest findings on vitamins and supplements to understand their evolving roles.
Frequently Asked Questions about Vitamins & Supplements
1. What’s the difference between vitamins & supplements?
Answer: Vitamins are essential organic compounds required for various bodily functions and are typically found in food. Supplements, however, are products designed to provide additional nutrients—such as vitamins, minerals, or other compounds—to support areas where dietary intake might be lacking.
2. Should I take a multivitamin every day?
Answer: It depends on your individual health needs. Multivitamins can help cover nutrient gaps, but if you already have a balanced diet, you may not need one. It’s best to consult with a healthcare provider to determine if a multivitamin would benefit you.
3. Can I get enough nutrients from food alone?
Answer: Ideally, yes. A well-balanced diet can provide most essential nutrients. However, dietary restrictions, certain health conditions, or limited food availability may make it difficult to obtain all necessary vitamins and minerals from food alone, in which case supplements may be beneficial.
4. Are there risks to taking too many vitamins & supplements?
Answer: Yes. Over-supplementation can lead to toxicity, especially with fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, and K), which are stored in the body. Excessive intake of minerals like iron and calcium can also pose health risks. Always follow recommended dosages and consult a healthcare professional if unsure.
5. What’s the best time of day to take vitamins?
Answer: This varies depending on the vitamin. Fat-soluble vitamins (A, D, E, K) absorb better with food, while water-soluble vitamins (C and B vitamins) can be taken on an empty stomach. Some people find it helpful to take multivitamins or minerals like magnesium before bed.
6. Are supplements regulated by the FDA?
Answer: Dietary supplements are not regulated as strictly as medications. The FDA oversees supplement safety but does not approve supplements before they go to market. For safety, choose brands that follow Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) and are third-party tested.
7. How can I know if I need supplements?
Answer: A blood test can reveal deficiencies, helping determine if supplements are necessary. If you experience symptoms like fatigue, muscle cramps, or frequent illness, you might benefit from certain vitamins or minerals, but it’s essential to consult a healthcare provider before starting.
8. Do vitamins and supplements have side effects?
Answer: Yes, they can. High doses of certain vitamins and minerals can cause nausea, digestive issues, and other side effects. For instance, too much iron can lead to constipation, while excess Vitamin C might cause diarrhea. Always start with recommended doses.
9. Can I take multiple supplements together?
Answer: Some supplements work well together, while others may interfere with each other’s absorption. For example, calcium and iron can inhibit each other if taken together, so it’s best to take them at different times. Consulting a healthcare provider for a tailored plan is ideal.
10. How long does it take to see benefits from supplements?
Answer: The time varies based on the supplement and the individual’s current health status. Some people notice improvements in a few weeks, while others might need several months to experience the benefits. Consistency is key with most supplements.
11. Can supplements replace a healthy diet?
Answer: No, supplements are designed to complement a healthy diet, not replace it. Whole foods contain a variety of nutrients, fiber, and phytochemicals that work together for optimal health, which cannot be fully replicated in supplement form.
12. Are there specific supplements recommended for certain age groups?
Answer: Yes, needs can vary by age. For example, children may benefit from Vitamin D and calcium for bone growth, while older adults might need extra Vitamin D, calcium, and Vitamin B12. Tailoring supplements to age and health conditions is beneficial.
Conclusion: The Role of Vitamins & Supplements in Modern Health
Vitamins & supplements can be beneficial allies in achieving a well-rounded, healthy lifestyle. They can fill nutritional gaps, support specific health needs, and help maintain a balanced life. However, they should not replace a healthy diet. The best results come from using supplements as part of a holistic approach that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and adequate rest.
References
- Council for Responsible Nutrition. “2024 CRN Consumer Survey on Dietary Supplements.” Retrieved from crnusa.org.
- National Institutes of Health Office of Dietary Supplements. “Dietary Supplement Fact Sheets.” Retrieved from ods.od.nih.gov.
- Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health. “Vitamins and Minerals.” Retrieved from hsph.harvard.edu.




